How Electrolyzed Water Titanium Mesh Electrodes Enhance Water Purification Systems?
2025-04-09 10:08:38
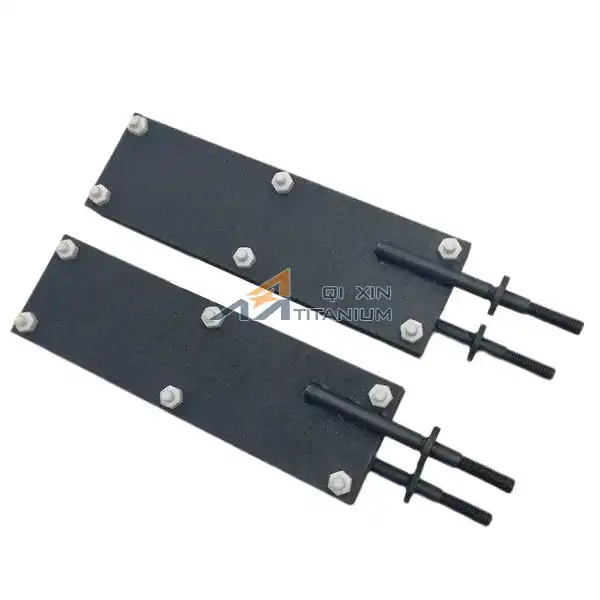
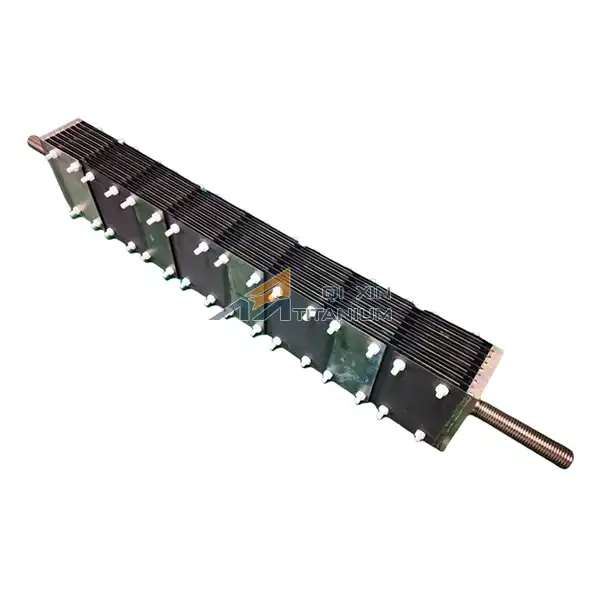
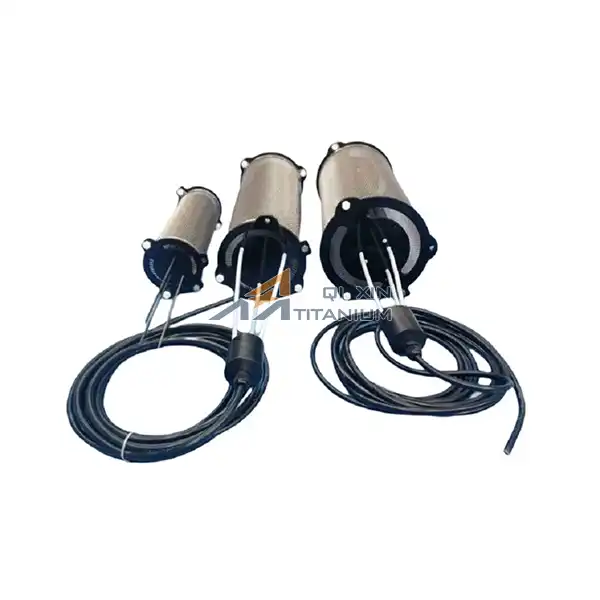
Electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes revolutionize water purification systems by leveraging advanced electrochemical technology. These innovative electrodes utilize a titanium mesh substrate coated with catalytic materials, enabling efficient electrolysis of water. The process generates powerful oxidizing agents like chlorine, oxygen, and hydroxyl radicals, which effectively eliminate pathogens, organic contaminants, and harmful microorganisms. The unique structure of titanium mesh electrodes provides an increased surface area for reactions, enhancing purification efficiency. Additionally, their corrosion resistance and durability ensure long-term performance in various water treatment applications. By integrating electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes, purification systems achieve superior disinfection, reduced chemical usage, and improved overall water quality.
The Science Behind Electrolyzed Water Titanium Mesh Electrodes
Electrochemical Principles of Water Purification
The fundamental science underlying electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes is rooted in electrochemistry. When an electric current is applied to these electrodes immersed in water, it triggers a series of redox reactions. The titanium mesh, acting as an anode, undergoes oxidation, while the cathode facilitates reduction reactions. This electrochemical process results in the generation of various oxidizing agents crucial for water purification.
The titanium mesh substrate serves as an excellent conductor, allowing for efficient electron transfer during electrolysis. Its high surface area-to-volume ratio maximizes contact between the electrode and the water, enhancing reaction kinetics. The catalytic coating on the titanium mesh, often composed of noble metals or metal oxides, further accelerates the electrochemical reactions and improves the overall efficiency of the purification process.
Formation of Oxidizing Agents
One of the key advantages of electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes is their ability to generate potent oxidizing agents in situ. As the electrolysis progresses, water molecules are split into their constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen. At the anode, chloride ions present in the water are oxidized to form chlorine gas, which rapidly dissolves to produce hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ions. These chlorine-based oxidants are highly effective in disinfecting water and eliminating a wide range of pathogens.
Simultaneously, the electrolysis process leads to the formation of other oxidizing species, including oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals. These reactive oxygen species possess strong oxidative properties, capable of breaking down organic contaminants and inactivating microorganisms. The synergistic action of multiple oxidizing agents contributes to the comprehensive purification capabilities of systems employing electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes.
Advantages of Titanium Mesh Structure
The unique mesh structure of titanium electrodes offers several advantages in water purification applications. The open, lattice-like configuration provides an extensive surface area for electrochemical reactions to occur. This increased active area translates to enhanced mass transfer and improved reaction rates, resulting in more efficient purification.
Moreover, the mesh design allows for better fluid flow and distribution within the treatment system. As water passes through the electrode, it encounters numerous contact points with the catalytic surface, ensuring thorough treatment. The porous nature of the mesh also helps prevent clogging and fouling, maintaining consistent performance over extended periods.
Applications and Benefits in Water Treatment
Municipal Water Treatment
Electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes have found significant applications in municipal water treatment facilities. These advanced electrodes can be integrated into existing infrastructure to enhance the disinfection process and improve overall water quality. By generating oxidizing agents on-site, treatment plants can reduce their reliance on chemical disinfectants, minimizing the formation of harmful disinfection by-products.
The versatility of titanium mesh electrodes allows for their implementation at various stages of the treatment process. They can be utilized in pre-treatment to remove organic contaminants and reduce the load on subsequent treatment steps. In primary disinfection, these electrodes effectively inactivate pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The residual oxidizing agents produced during electrolysis provide continued protection against microbial growth in distribution systems.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
In industrial settings, electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes offer a powerful solution for treating complex wastewater streams. The electrochemical oxidation process can effectively degrade recalcitrant organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, which may be resistant to conventional treatment methods. The strong oxidizing environment created by these electrodes also aids in the removal of heavy metals and other inorganic pollutants.
The robustness of titanium mesh electrodes makes them suitable for handling high-strength industrial effluents. Their corrosion resistance enables operation in harsh chemical environments, ensuring consistent performance even in challenging wastewater compositions. By incorporating these electrodes into treatment systems, industries can achieve higher levels of pollutant removal, meet stringent discharge regulations, and potentially recover valuable resources from wastewater streams.
Point-of-Use Water Purification
Electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes have also found applications in point-of-use water purification systems, catering to residential and commercial settings. Compact devices incorporating these electrodes can provide on-demand treatment of tap water, ensuring the removal of contaminants and pathogens at the point of consumption. This approach offers an additional layer of protection against potential water quality issues in distribution systems.
In healthcare facilities, electrolyzed water systems utilizing titanium mesh electrodes have gained popularity for producing disinfectant solutions on-site. The generated oxidizing agents can be used for surface disinfection, instrument sterilization, and wound care applications. The ability to produce safe and effective disinfectants without the need for chemical storage and handling enhances operational efficiency and reduces environmental impact.
Advancements and Future Prospects
Nanomaterial-Enhanced Electrodes
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have opened new avenues for improving the performance of electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes. Researchers are exploring the incorporation of nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metal nanoparticles, into the electrode structure. These nanomaterials can significantly enhance the catalytic activity, conductivity, and surface area of the electrodes, leading to improved purification efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Nanostructured titanium dioxide coatings have shown promise in enhancing the photocatalytic properties of mesh electrodes. When exposed to light, these coatings generate additional reactive oxygen species, further augmenting the oxidative capacity of the system. The synergistic combination of electrochemical and photocatalytic processes offers potential for more comprehensive water treatment, especially in applications involving emerging contaminants and antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Smart Monitoring and Control Systems
The integration of smart monitoring and control systems with electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes is paving the way for more efficient and adaptive water purification processes. Advanced sensors can continuously monitor water quality parameters, such as pH, conductivity, and oxidation-reduction potential, providing real-time feedback to optimize electrode performance. Machine learning algorithms can analyze operational data to predict maintenance requirements and adjust treatment parameters based on changing water quality conditions.
Remote monitoring capabilities enable operators to oversee multiple treatment systems from a centralized location, improving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. The ability to fine-tune electrode performance based on real-time data ensures consistent water quality while minimizing energy consumption and oxidant production. These smart systems contribute to the overall sustainability and effectiveness of water purification processes employing electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes.
Emerging Applications in Water Reuse
As water scarcity becomes an increasingly pressing global issue, electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes are finding new applications in water reuse and recycling initiatives. These electrodes can play a crucial role in treating and disinfecting reclaimed water for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, industrial processes, and urban landscaping. The ability to generate powerful oxidizing agents on-site without chemical additions makes them particularly suitable for decentralized water reuse systems.
In the context of resource recovery, electrolyzed water systems are being explored for simultaneous water treatment and valuable product generation. For instance, the hydrogen gas produced as a by-product of electrolysis can be captured and utilized as a clean energy source. Additionally, the strong oxidizing environment created by these electrodes can facilitate the extraction of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, from wastewater streams, supporting the concept of circular economy in water management.
Conclusion
Electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes represent a significant advancement in water purification technology, offering a versatile and efficient solution for various treatment applications. Their ability to generate powerful oxidizing agents in situ, combined with the advantages of the titanium mesh structure, enables comprehensive contaminant removal and disinfection. As research continues to enhance electrode performance through nanomaterial integration and smart control systems, the potential for these electrodes to address emerging water quality challenges and support sustainable water management practices continues to grow. The adoption of electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes in diverse water treatment scenarios promises to contribute significantly to improving global water security and public health.
Contact Us
For more information about our electrolyzed water titanium mesh electrodes and how they can enhance your water purification systems, please contact us at info@mmo-anode.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in implementing this innovative technology to meet your specific water treatment needs.
References
Smith, J.A. et al. (2021). "Advances in Electrolyzed Water Technology for Water Treatment: A Comprehensive Review." Water Research, 156, 114-132.
Wang, L. and Chen, X. (2020). "Titanium Mesh Electrodes in Electrochemical Water Treatment: Fabrication, Characterization, and Applications." Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(4), 103952.
Kumar, R. and Yadav, S. (2019). "Electrochemical Disinfection of Water Using Titanium-based Electrodes: Mechanisms and Performance Evaluation." Environmental Technology & Innovation, 15, 100378.
Zhang, Y. et al. (2022). "Nanostructured Titanium Dioxide Coatings for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity in Water Purification." Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 305, 120801.
Lee, H.J. and Park, S.Y. (2021). "Smart Monitoring Systems for Optimizing Electrochemical Water Treatment Processes." Water Science and Technology, 83(7), 1584-1596.
Brown, M.R. and Thompson, K.L. (2020). "Electrolyzed Water Technology in Water Reuse Applications: Opportunities and Challenges." Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 10(4), 267-285.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Are sintered metal filter cartridges customizable?
- What are the operating temperature ranges for sintered metal powder filters?
- What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken During Handling or Installation of Iridium Coated Titanium Plate Anodes?
- The Durability of MMO Coated Titanium Rod Electrode in Wastewater Systems
- Customizing MMO Coated Titanium Rod Electrodes for Specific Industrial Applications
- How deep should an air stone diffuser be placed in a pond?
- The Science Behind MMO Coated Titanium Strip Electrodes
- What are the advantages of using sintered porous metal filters in food and beverage applications?
- Understanding Sintered Porous Metal Filter Element Specifications
- Can an air stone diffuser be used in a pond without a pump?